Rivers app: ArcGIS API for JavaScript
I built a web application to understand the contribution of rivers that originate or flow through protected areas.
Using Jupyter notebooks and a global river dataset from a study that mapped the world's free-flowing rivers, I packaged the results using ArcGIS API for JavaScript.
The code for the analysis is available here.
First, import the relevant libraries
import geopandas as gpd
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import shapely.geometry
import shapely.ops
import pandas as pd
import folium
import earthpy
from ipyleaflet import Map, GeoData, basemaps, LayersControl
import json
from ipywidgets import HTML
import numpy as np
import multiprocessing
import time
from functools import partial
Create a buffer around protected areas
parks = gpd.read_file("../../data/rivers/Polygon_layer.shp").to_crs(epsg=4269)
for index, park in parks.iterrows():
print(park.loc['name'])
park_name = 'Majete Wildlife Reserve'
# Buffer
park_buffer = parks.loc[parks['name'] == park_name].to_crs('+proj=sinu +lon_0=0 +x_0=0 +y_0=0 +ellps=WGS84 +datum=WGS84 +units=m +no_defs ')
park_buffer['geometry'] = park_buffer['geometry'].geometry.buffer(500000)
park_buffer = park_buffer.to_crs(epsg=4269)
# Park
park = parks.loc[parks['name'] == park_name].to_crs('+proj=sinu +lon_0=0 +x_0=0 +y_0=0 +ellps=WGS84 +datum=WGS84 +units=m +no_defs ')
park['geometry'] = park['geometry'].geometry.buffer(500)
park = park.to_crs(epsg=4269)
Identify rivers inside protected areas
# Rivers
try:
rwa_rivers
except NameError:
rwa_rivers = gpd.read_file("../../data/rivers/clipped_rivers.shp").to_crs(epsg=4269)
# Buffer rivers
buffer_border = gpd.GeoDataFrame(geometry=park_buffer.boundary)
buffer_rivers = gpd.sjoin(rwa_rivers, park_buffer, how='inner', predicate='within')
# Park rivers
park_rivers = gpd.sjoin(rwa_rivers, park, how='inner', predicate='within')
park_rivers = park_rivers.reset_index(drop=True)
# Set property if in park
buffer_rivers['inpark_par'] = 0
for index1, river1 in buffer_rivers.iterrows():
if river1['NOID'] in park_rivers['NOID'].values:
buffer_rivers.at[index1, 'inpark_par'] = 1
buffer_rivers = buffer_rivers.rename(columns={'index_left': 'i_l'})
buffer_rivers = buffer_rivers.rename(columns={'index_right': 'i_r'})
buffer_rivers = buffer_rivers.reset_index(drop=True)
# Rivers entering the park from outside
buffer_rivers['o_outside_dis']=0.0
buffer_rivers['o_inflow_par']=0
buffer_rivers['o_through_par']=0
buffer_rivers['o_park_dis']=0.0
# Rivers starting in park
buffer_rivers['i_start_dis']=0.0
buffer_rivers['i_park_dis']=0.0
buffer_rivers['i_park_fra']=0.0
# All rivers
buffer_rivers['park_dis']=0.0
buffer_rivers['intersect_par'] = 0
buffer_rivers['park_fra']=0.0
# Rivers on boundary of park
park_rivers['intersect_par'] = 0
park_rivers['o_outside_dis']=0.0
buffer_rivers['o_park_fra']=0.0
park_border = gpd.GeoDataFrame(geometry=park.boundary)
all_inters = gpd.sjoin(buffer_rivers, park_border, op='intersects')
Set properties for river segments
for index1, river1 in buffer_rivers.iterrows():
if river1['NOID'] in all_inters['NOID'].values:
buffer_rivers.at[index1, 'intersect_par'] = 1
buffer_rivers.at[index1, 'inpark_par'] = 1
for index1, river1 in buffer_rivers.iterrows():
if river1['NOID'] in park_rivers['NOID'].values:
buffer_rivers.at[index1, 'inpark_par'] = 1
for index1, river1 in all_inters.iterrows():
if river1['NOID'] in park_rivers['NOID'].values:
park_rivers.at[index1, 'intersect_par'] = 1
all_inters = all_inters.reset_index(drop=True)
inters = gpd.GeoDataFrame()
for index1, r1 in all_inters.iterrows():
already_intersected = 0
for index2, r2 in all_inters.iterrows():
if r1['NOID'] == r2['NDOID']:
already_intersected = 1
if already_intersected != 1:
inters = inters.append(all_inters.iloc[index1])
# Make df of all rivers inside and intersecting park
in_park = park_rivers.append(inters)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set_aspect('equal')
buffer_rivers.plot(ax=ax, color='grey')
park_border.plot(ax=ax, color='red')
in_park.plot(ax=ax, color='orange')
# inters.plot(ax=ax, color='blue')
plt.show();
Find upstream river outside park
in_inters = gpd.GeoDataFrame()
inters = inters.reset_index(drop=True)
# Loop through all rivers intersecting with park border
for index1, r1 in inters.iterrows():
# All rivers starting
if r1['NUOID'] is None:
pass
# All rivers not starting
else:
for index2, r2 in buffer_rivers.loc[buffer_rivers['NDOID']==r1['NOID']].iterrows():
# If river (r2) flows into river on border (r1)
if r1['NOID'] == r2['NDOID']:
# to make sure upstream river (r2) is outside the park
if r2['inpark_par'] != 1:
# then upstream river (r2) is flowing into the park
inters.at[index1, 'o_inflow_par'] = 1
in_inters = in_inters.append(inters.iloc[index1])
print(inters.loc[inters['o_inflow_par']==1,'NOID'])
# Set the o_inflow_par of buffer_rivers also to 1
buffer_rivers.loc[buffer_rivers['NOID'].isin(inters.loc[inters['o_inflow_par']==1,'NOID']), 'o_inflow_par'] = 1
# If there are rivers flowing into the park
if in_inters.shape[0] > 0:
# drop all duplicate in-flowing rivers
in_inters = in_inters.drop_duplicates()
print('Number of inflowing rivers: ' + str(len(in_inters)))
# set property on buffer_rivers to know that river is entering the park from outside
# may be REDUNDANT
for index1, river1 in buffer_rivers.iterrows():
if river1['NOID'] in in_inters['NOID'].values:
buffer_rivers.at[index1, 'o_inflow_par'] = 1
# plot to show in-flowing rivers
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set_aspect('equal')
park_border.plot(ax=ax, color='grey')
park_rivers.plot(ax=ax, color='black')
inters.plot(ax=ax, color='blue')
in_inters.plot(ax=ax, color='red')
plt.show();
Continuing
Next, we find upstream rivers outside protected areas, calculating the outside flow and calculate the protected area contribution to each segment. Finally, we combine the results with rivers starting in the protected areas.
The full code is available here.
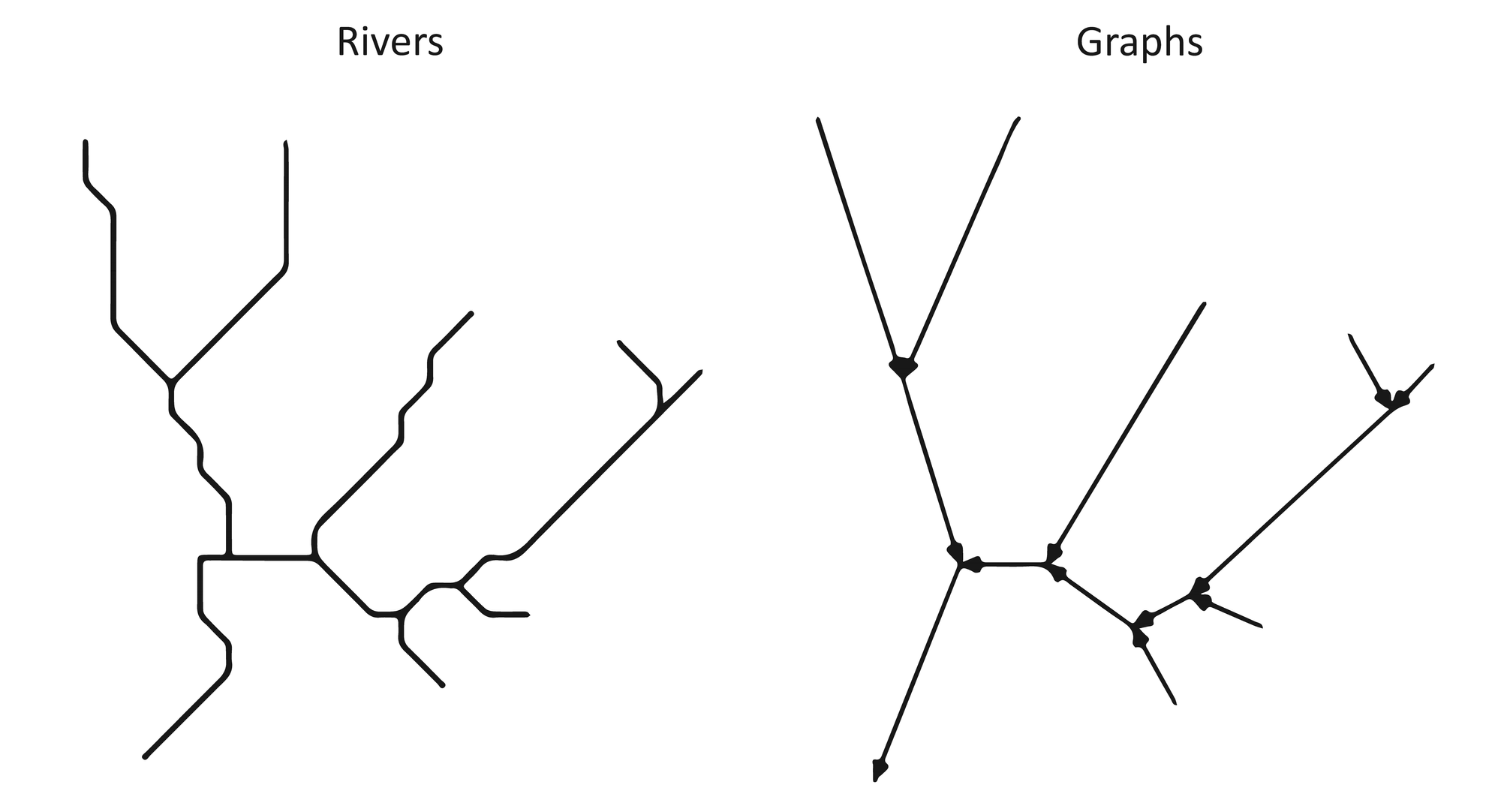
Next up
The current way to analyse these rivers results in for loops within for loops within for loops and is quite inefficient. An alternative that I'm exploring is, to borrow from network theory and map rivers as a graph network where river segments represent links and the confluence between them represents the nodes. There are many helpful python libraries for network analysis networkx.